Teknologian suunnittelu ja ohjelmointi
Lukuaika noin 14 minuuttia

Lukuaika noin 14 minuuttia
Teknologia on se runsaudensarvi, joka on tuonut ihmiskunnan nälänhädän, ydinsodan, raaka-ainepulan ja kulkutautien keskeltä kohti kestävää laajalle levinnyttä vaurautta. Automaattinen tietojenkäsittely on yksi menneen vuosisadan menestystarinoista. Työnantajien pettymykseksi tapaa kouluttaa halpoja ohjelmoijia ei ole yrityksistä huolimatta löydetty.
Uuden teknologian kehittäminen on luonnostaan vaikeaa. Tutkimuksessa ja tuotekehityksessä lopputulos ei ole ennustettavissa eikä ole edes varmaa, että se on saavutettavissa. Teknologiat perustuvat luonnontieteisiin ja matematiikkaan, jotka ovat eksakteja tieteenaloja. Luonnonlait ovat olemassa ihmisestä riippumatta ja jos suunnitelmamme ei kunnioita niitä, ratkaisu ei toimi.
Onnistuminen teknologian kehittämisessä vaatii monien vaikuttavien tekijöiden sovittamista samaan ratkaisuun. Ajatellaanpa vaikka akkuja lentokoneen energiavarastona. Akun pitää olla mm. kevyt, hinnaltaan kohtuullinen, kapasiteetiltaan riittävä ja olla ladattavissa nopeasti. Sen elinkaaren pitää olla pitkä ja mahdollisimman huoltovapaa. Se ei saa olla vaarallinen onnettomuuksissa eikä etenkään itse aiheuttaa vaaraa ihmisille ja omaisuudelle. Voi jopa olla, että energian varastointi ioneihin ei pysty korvaamaan sen kuljettamista kemiallisina yhdisteinä kuten polttoaineina käytettyinä hiilivetyinä.
Ohjelmistojen kehittämisessä ei ole odotettavissa suuria tuottavuusloikkia, koska vaikeus on ajattelussa, ei koodin kirjoittamisessa [1]. Ongelma on sama kuin kirjan kirjoittamisessa. Vaikeinta on päättää, mitä kirjoittaa. Paremmat tekstinkäsittelyohjelmat eivät tee kenestäkään Nobel-kirjailijaa. Tekstinkäsittelyn ulkoistaminen halpatyövoimalle ei todennäköisesti vähentäisi kirjoittamisen kokonaiskustannuksia.
Luonnontieteet perustuvat havaintoihin. Jos teoriasi ei vastaa havaintoja, se on väärin, olitpa kuinka kuuluisa ja arvostettu tiedemies tahansa. Suunnittelutyössä luotamme aiempiin havaintoihin ja niistä syntyneeseen kokemukseen. Sillat, katot ja tornitalot sortuvat harvoin, koska samanlaisia on rakennettu miljoonia jo aiemmin.
Kokemus on kirjattu standardeihin ja tällöin pääpaino keskittyy niiden noudattamisen valvontaan. Standardien kääntöpuolena on luovuuden kahlitseminen. Uusia innovaatioita on vaikea tuoda markkinoille, koska standardien muuttaminen on vaikean byrokratian takana. Standardit estävät uudenlaisten kilpailijoiden tuloa markkinoille.
Sääntelyä perustellaan useimmiten kuluttajien suojelemisella. Hyvää tavoittelevilla säännöksillä on saatu paljon vahinkoa aikaan kun ne on tehty ilman riittävää havaintoaineistoa. Homeiset koulut ovat esimerkki, jossa rakennusten tiivistäminen aiheuttaa kosteuden kertymistä rakenteisiin.
Matematiikassa keskeistä on looginen eheys. Myös teknologiaratkaisujen pitää muodostaa keskenään ristiriidaton kokonaisuus. Ihmiset kokevat epämukavana [2] esimerkiksi hiilivedyistä tuotetun vedyn käytön polttoaineena hiilivetyjen käytön välttämiseksi.
Ohjelmistotuotannossa ohjelmoijat tekevät suuren määrän testejä, jotka tarkistavat koodilogiikan toimivuutta. Nykyään testien ajaminen automatisoidaan, jolloin testauskustannus muodostuu pääosin testien kirjoittamisesta.
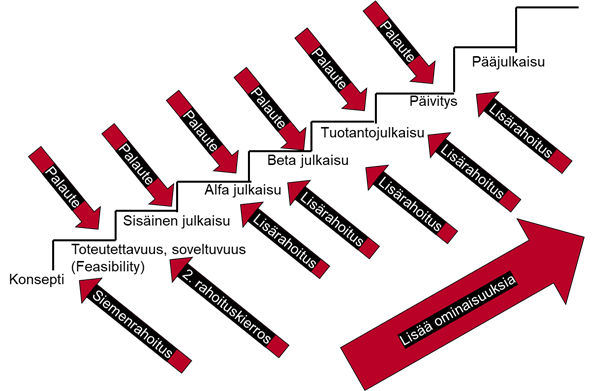
Uuden tuotteen suunnittelu etenee tyypillisesti idean varmistamisesta useiden prototyyppien kautta kohti varovaisesti julkaistavaa tuotetta. Tuotteen ominaisuuksien ja käyttäjien määrä kasvaa kehitystyön jatkuessa. Suuri osa tuotekehityshankkeista lopetetaan lähes alkuunsa. Ennen kuin esimerkiksi itseohjautuva auto saadaan lopullisesti markkinoille on sitä testattu miljoonia tunteja ja sillä on ajettu miljardeja kilometrejä erilaisissa ympäristöissä.
McKinseyn kyselyn mukaan yritysjohtajat ovat tyytymättömiä organisaatioidensa innovaatiokykyyn Yrityskulttuuri ja tapa toimia ei luo olosuhteita, joissa ihmiset voisivat tehdä jotakin erilaista [3].
Yliopistoissa aiemmin vallinnut akateeminen vapaus on korvautunut tiukalla tulosohjauksella. Työsuhteet ovat lyhytaikaisia ja epävarmoja. Julkaisujen määrää käytetään mittarina tuloksista. Tämän seurauksena on suuri määrä varmoja tutkimusaiheita, joista saa helposti tuotettua julkaisuja, jotka menevät vertaisarvioinnista läpi.
Yksi patenttitoimistojen virkailija tuotti sata vuotta sitten enemmän merkittävää tutkimusta kuin miljoonat päätoimiset tutkijat hänen jälkeensä [4]. Hän onnistui vakuuttamaan kriittisen tiedeyhteisön teorioitansa tukevien havaintojen avulla.
Toisinajattelijat luovat merkittävät uudet keksinnöt sananmukaisesti, koska merkittävät uudet keksinnöt vaativat toisenlaista ajattelua. Katso myös [5]. Useat organisaatiot korostavat yhdenmukaisuutta. Prosesseja standardoidaan tehokkuuden optimoimiseksi. Työtavat jäädytetään laatukäsikirjoilla. Henkilöstöhallinto palkitsee tottelevaisuudesta ja rankaisee poikkeamista. Epäonnistuminen johtaa henkilövaihdoksiin.
Toisinajattelu on vaikeaa, koska yhteisö luo kovan paineen sitä vastaan. Julkaisujen portinvartijat sensuroivat erilaisuutta. Sananvapautta kahlitaan. Uran eteneminen voi olla vaikeaa. Palkkio onnistumisesta on pieni, jos sitä on ollenkaan.
Tunnistamme asiat, joista ei saa puhua. Niiden taustalla on usein raha ja eturistiriidat. Innovaattorin dilemma selittää, miksi oman tuotteen kanssa kilpailevien tuotteiden kehittäminen onnistuu helpommin pieniltä ulkopuolisilta yrityksiltä [7]. Siispä internet-puhelut tulivat Skypeltä eikä teleoperaattoreilta.
Geneettinen erilaisuus on luonnon tapa selvitä koko ajan muuttuvassa ympäristössä. Jos ravinnosta on puutetta, pienemmät eläimet selviävät paremmin. Jos taas ravintoa on runsaasti, suosii luonnonvalinta isompia eläimiä.
Teknologiset ratkaisut ovat osa kompleksisia keskenään kilpailevia ekosysteemejä. Niillä on usein arvaamattomia pitkän tähtäyksen vaikutuksia, jotka mitätöivät lyhyen tähtäyksen hyödyt. Lähes kaikki suuret teknologiaorganisaatiot työskentelevät monien teknologiatoimittajien, integraattorien ja myyjien kanssa – joskus satojen niiden kanssa [7]. Monestikin mukautettavuus on lyhyen tähtäyksen kustannushyötyjä tärkeämpää.
Laajemmaltikin ajateltuna keskitetty päätöksenteko ja keskitetyt ratkaisut sisältävät suuria riskejä. Hajautetussa mallissa kaikki munat eivät ole samassa korissa. Kompleksisessa maailmassa emme pysty ennustamaan voittajia. Hajauttamalla niin sijoituksemme kuin teknologiaratkaisumme vähennämme riskejämme.
Historiasta opimme, että kansakunnat menestyvät kun kuluttajien tekemät ostopäätökset ohjaavat teknologioiden kehittämistä ja tuotantoa [8]. Vaihtoehtoisia tuotteita on suuri kilpaileva joukko ja omalla rahallaan ostavat ovat kriittisiä valintojensa suhteen. Massiivisella mielikuvamarkkinoinnilla tyrkytetyt vaihtoehdot hyödyttävät enimmäkseen myyjätahoja. LED-valot tulivat nopeasti ja huomaamatta käyttöön, koska ne kelpasivat kuluttajille luonnostaan. Sähköautojen eteneminen sen sijaan takkuaa suurista tukiaisista huolimatta.
Ohjelmoijapulan taustalla on se, että työnantajat eivät näe metsää puilta. Työpaikkailmoitukset ovat täynnä vaatimuksia tekniikoista, joiden osaamista edellytetään. Koska muodissa olevat tekniikat muuttuvat koko ajan, ei niiden kokeneita osaajia voi olla olemassa.
Kilpailutukset tuntihinnalla suosivat halpoja työntekijöitä, jotka ovat oppineet halutut asiat pinnallisesti. Jos kaikessa ohjelmoinnissa vaadittava looginen ajattelutapa puuttuu, ovat tulokset huonoja ja seuraavan tekniikan oppiminen on vaikeaa.
Nykypäivän hyvinvointi syntyy osaamisesta ja hyvistä ideoista. Raaka-aineista, rahoituksesta ja työvoimasta ei ole pulaa. Hallitusten pitäisi rahan lähettämisen sijaan edistää koko ihmiskunnan kouluttautumista. Vanhan vertauskuvan sanoin: älä anna nälkäiselle miehelle kalaa, vaan opeta hänet kalastamaan.
– Pentti Virtanen
1. Fred Brooks, The mythical man-month, 1975.
2. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cognitive_dissonance
3. https://hbr.org/2019/11/breaking-down-the-barriers-to-innovation
4. https://www.ige.ch/en/about-us/the-history-of-the-ipi/einstein/einstein-at-the-patent-office
5. Asko M. Aurela: Tieteellisen toisinajattelijan käsikirja, Art House, 1993.
6. https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/building-a-tech-services-ecosystem-to-deliver-products-not-applications
7.Innovaattorin dilemma https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Innovator%27s_Dilemma
8. https://whynationsfail.com/summary/
Kun osallistut MIF Tutkintojen, Johtamistaidon opisto JTO:n, Inforin, Fintran tai MIF Academyn koulutuksiin, pääset kouluttautumaan tulevaisuuden osaajaksi ennen muita!
Technology is the cornucopia that has brought mankind from famine, nuclear war, shortage of raw materials and epidemics towards sustainable widespread prosperity. Automatic data processing is one of the success stories of the past century. To the disappointment of employers, the way to train cheap programmers has not been found, despite attempts.
Developing new technologies is inherently difficult. In research and development, the end result is not predictable and it is not even certain that it is achievable. Technologies are based on natural sciences and mathematics, which are exact disciplines. The laws of nature exist regardless of man, and if our plan does not respect them, the solution will not work.
Success in technological development requires adapting many influential factors of the same solution. Let’s think of batteries as an airplane energy storage. The battery must be lightweight, reasonable in price, sufficient in capacity and it can be rechargeable quickly. Its life cycle must be long and as maintenance-free as possible. It must not be dangerous in the case of accidents, and in especially not in itself, pose a danger to people and property. It may even be that storing energy in ions cannot replace its transport as chemical compounds such as hydrocarbons used as fuels.
No major productivity leaps are expected in software development, as the difficulty is in thinking, not in writing code[1]. The problem is the same as writing a book. The hardest part is deciding what to write. Better word processors do not make anyone a Nobel writer. Outsourcing word processing to low-cost labor is unlikely to reduce the total cost of writing.
Natural sciences are based on observations. If your theory doesn’t match the findings, it’s wrong, no matter how famous and respected you are. In our design work, we rely on previous observations and the experience gained from them. Bridges, roofs and high-rises rarely collapse because millions of similar ones have been built before.
Experience is enshrined in standards, and the focus is on monitoring compliance with them. The other side of the standards is the shackle of creativity. It is difficult to bring new innovations to market because changing standards is behind difficult bureaucracy. The standards prevent new competitors from entering the market.
Regulation is most often justified by the protection of consumers. Good-seeking regulations have done a lot of damage when they have been made without sufficient observational data. Mouldy schools are an example where making buildings air-tight causes moisture to accumulate in structures.
Logical integrity is central to mathematics. Technology solutions must also form a consistent whole. People find it uncomfortable [2] to use hydrogen from hydrocarbons as fuel to avoid the use of hydrocarbons, for example.
In software production, programmers perform a large number of tests that check the functionality of code logic. Nowadays, the driving of tests is automated, which means that the testing cost consists mainly of writing tests.
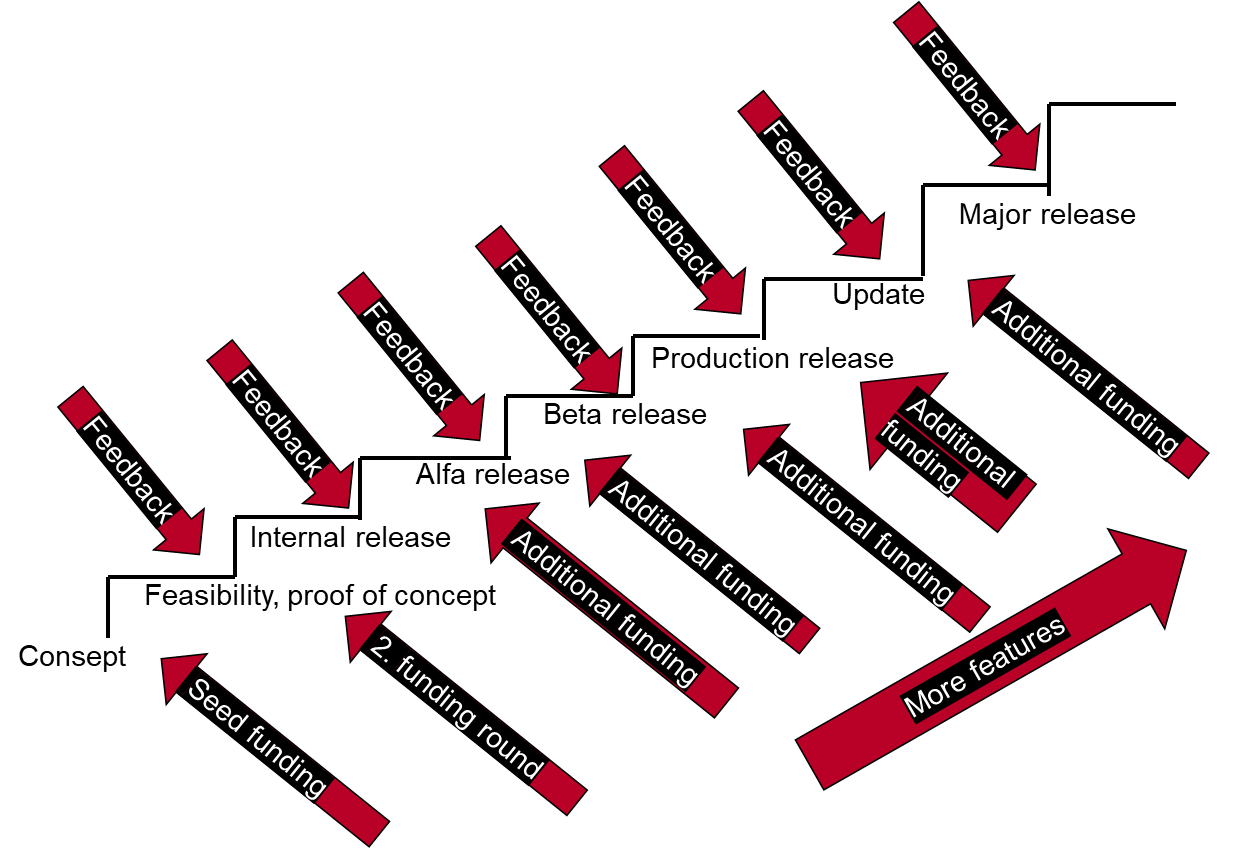
Designing a new product typically proceeds from ensuring the idea through several prototypes towards a product that is cautiously released. The number of product features and users increases as the development continues. A large number of R&D projects are fail fast. Before, for example, a self-driving car is finally placed on the market, it has been tested for millions of hours and it has driven billions of kilometers in various environments.
According to McKinsey’s survey, business leaders are dissatisfied with their organizations’ ability to innovate. Company culture and the way they operate does not create conditions in which people could do something different [3].
Academic freedom in universities in the past has been replaced by strict performance guidance. Employment relationships are short-term and precarious. The number of publications is used as a measure of the results. As a consequence, there are a large number of certain research topics that can easily produce publications that go through peer review.
One patent office clerk produced more significant research a hundred years ago than millions of full-time researchers since him [4]. He managed to convince the critical scientific community through observations supporting his theories.
Dissidents create significant new inventions because significant new inventions require different thinking. See also [5]. Several organizations emphasize unity. Processes are standardized to optimize efficiency. Working methods are frozen with quality manuals. HR rewards obedience and punishes deviations. Failure leads to personal changes.
Dissent is difficult because the community creates a lot of pressure against it. The gatekeepers of publications censor differences. Freedom of speech is being shackled. Career progression can be difficult. The reward for success is small, if there is any.
We recognize things that are not allowed to be talked about. They are often driven by money and conflicts of interest. The innovator’s dilemma explains why it is easier for small external companies to develop products that compete with your own product [7]. So the internet calls came from Skype and not from telecommunications operators.
Genetic diversity is nature’s way of surviving in an ever-changing environment. If there is a lack of food, smaller animals will survive better. If, on the other hand, there is plenty of food, natural selection favors larger animals.
Technological solutions are part of complex competing ecosystems. They often have unpredictable long-term effects that nullify the short-term benefits. Almost all major technology organizations work with many technology suppliers, integrators and vendors – sometimes hundreds of them [7]. In many cases, adaptability is more important than short-term cost benefits.
Even more broadly, centralized decision-making and centralized solutions involve great risks. In a decentralized model not all eggs are in the same basket. In a complex world, we can’t predict winners. By diversifying both our investments and our technology solutions, we reduce our risks.
We learned from history that nations thrive when consumers’ purchasing decisions guide the development and production of technologies [8]. There is a large competing group of alternative products and those buying with their own money are critical to their choices. Alternatives imposed by massive image marketing mostly benefit sellers. LED lights came into use quickly and undetected because they were good enough for consumers naturally. The advancement of electric cars, on the other hand, is slowing despite the high subsidies.
Genetic diversity is nature’s way of surviving in an ever-changing environment. If there is a lack of food, smaller animals will survive better. If, on the other hand, there is plenty of food, natural selection favours larger animals.
The underlying reason for the programmer shortage is that employers do not see the forest from the trees. Job advertisements are full of requirements for techniques whose skills are required. Because fashionable techniques are constantly changing, their experienced experts cannot exist.
Competitive tendering at the hourly rate favors cheap workers who have learned the desired things superficially. If the logical mindset required for all programming is lacking, the results are poor and learning the next technique is difficult.
Today’s well-being comes from knowledge and good ideas. There is no shortage of raw materials, funding and labor. Instead of sending money, governments should promote the education of all mankind. In the words of an old metaphor: do not give a hungry man fish, but teach him how to fish.
– Pentti Virtanen
1. Fred Brooks, The mythical man-month, 1975.
2. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cognitive_dissonance
3. https://hbr.org/2019/11/breaking-down-the-barriers-to-innovation
4. https://www.ige.ch/en/about-us/the-history-of-the-ipi/einstein/einstein-at-the-patent-office
5. Handbook of Scientific Dissidents: Asko M. Aurela: Tieteellisen toisinajattelijan käsikirja, Art House, 1993.
6. https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/building-a-tech-services-ecosystem-to-deliver-products-not-applications
7. Innovator’s dilemma https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Innovator%27s_Dilemma
8. https://whynationsfail.com/summary/
When you participate in MIF Tutkinnot, Johtamistaidon opisto JTO, Infor, Fintra or MIF Academy trainings, you will train yourself as a future expert before others